Allergies to certain foods are common and can cause a variety of symptoms. Potatoes are a staple food in many diets and are typically consumed cooked, but can you be allergic to raw potatoes but not cooked?
While it is rare, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction specifically to raw potatoes. This type of allergy is known as oral allergy syndrome, or OAS. OAS is a condition where the immune system reacts to proteins in certain fruits, vegetables, and nuts. In the case of raw potatoes, the main culprit is believed to be a protein called patatin, which is found in higher levels in uncooked potatoes.
Symptoms of a raw potato allergy may include itching, tingling, or swelling of the lips, tongue, and throat. Some individuals may also experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, or diarrhea. In severe cases, a raw potato allergy can lead to anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
Interestingly, many individuals with a raw potato allergy may be able to tolerate cooked potatoes without experiencing any adverse reactions. This is because cooking alters the proteins in potatoes, potentially reducing their allergenicity. However, it is important to note that some individuals may still react to cooked potatoes due to cross-reactivity with other foods or individual sensitivities.
It is important for individuals who suspect an allergy to raw or cooked potatoes to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance.
If you suspect you have a raw potato allergy, it is best to avoid consuming raw potatoes and any products that may contain them. It is also important to read food labels carefully, as potatoes can be present in various processed foods in different forms. If you are unsure about a particular food or dish, it is always better to err on the side of caution and avoid it.
In conclusion, while it is possible to be allergic to raw potatoes but not cooked, this type of allergy is relatively rare. If you suspect a potato allergy, it is important to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the best course of action to manage and avoid potential allergic reactions.
Raw Potato Allergy: Symptoms and Causes
Allergies to raw potatoes are rare but can occur in some individuals. While most people can consume cooked potatoes without any adverse reactions, a small percentage may experience allergic symptoms specifically when exposed to raw potatoes.
Symptoms of Raw Potato Allergy
When someone with a raw potato allergy comes into contact with raw potatoes or consumes them, they may experience a range of symptoms. These symptoms can include:
| Common Symptoms | Less Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| – Itching | – Nausea |
| – Hives or skin rash | – Abdominal pain |
| – Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat | – Vomiting |
| – Difficulty breathing or wheezing | – Diarrhea |
If any of these symptoms occur after consuming raw potatoes, it is important to seek medical attention, as severe allergic reactions can be life-threatening.
Causes of Raw Potato Allergy
The exact cause of raw potato allergy is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the presence of certain proteins found in raw potatoes. These proteins can trigger an immune response in individuals with a sensitivity or allergy to them.
Cooking potatoes can alter the structure of these proteins, making them less likely to cause an allergic reaction. This is why some individuals may be able to tolerate cooked potatoes but not raw ones.
It is worth noting that an allergy to raw potatoes does not necessarily mean an allergy to all members of the potato family, such as sweet potatoes or yams. Each type of potato has distinct proteins, and allergies can vary from person to person.
Cooked Potato Allergy: Is it Possible?
Allergies to food can be complex and varied. Some individuals may have allergies to specific types of food, while others may have allergies to certain food preparations. It is not uncommon for individuals to develop allergies to raw foods, such as fruits or vegetables. However, can a person have an allergy to raw potatoes and not cooked ones? Let’s explore this topic further.
The Science Behind Allergies
Allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance as a threat. This triggers an immune response, leading to the release of histamines and other chemicals that cause allergy symptoms. In the case of food allergies, the immune system reacts to proteins found in the food.
Raw Potato Allergy
Raw potatoes contain proteins known as patatins, which have been found to cause allergies in some individuals. Symptoms of a raw potato allergy can include itching, hives, swelling, and digestive issues. If you suspect a raw potato allergy, it is important to avoid consuming raw potatoes and any raw potato products.
Cooked Potato Allergy
While it is rare, some individuals may develop an allergy to cooked potatoes even if they can tolerate raw potatoes. This may be due to the denaturation of patatins during the cooking process, which can cause changes in the protein structure. Cooking methods such as baking or boiling can alter the proteins in the potato, potentially triggering an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals.
Managing Potato Allergies
If you suspect an allergy to raw or cooked potatoes, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. They can perform tests, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, to determine if you have an allergy. If you are diagnosed with a potato allergy, it is essential to avoid consuming potatoes or any products containing potatoes.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional if you have any health concerns or questions.
Food Allergies and Cross-Reactivity
Food allergies occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies certain proteins in food as harmful substances. These proteins, known as allergens, can trigger an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals. While many food allergies are specific to certain types of foods, cross-reactivity can also occur.
Cross-reactivity happens when the immune system reacts to proteins in one food that are similar to proteins in another food. For example, someone who is allergic to raw potatoes may also experience symptoms after consuming cooked potatoes. This is because the proteins in raw and cooked potatoes are similar enough to trigger an immune response in individuals who are allergic to potatoes.
The reason behind cross-reactivity is that proteins in different foods can have similar structures or sequences of amino acids. This similarity can lead to the immune system mistaking one protein for another and triggering an allergic reaction. Cross-reactivity can occur not only between raw and cooked forms of the same food but also between different foods within the same family. For instance, someone who is allergic to birch pollen may also experience allergy symptoms after consuming apples or certain tree nuts.
It is important for individuals with food allergies to be aware of potential cross-reactivity and to take precautions to avoid triggering allergic reactions. This may involve avoiding not only the specific food that triggers an allergy but also related foods that may cause cross-reactivity. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or allergist for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Common Allergens and their Potential Relationship to Potato Allergy
Allergies to various foods are fairly common, and potatoes can be one such allergen that some individuals may be sensitive to. It is important to note that an allergic reaction to raw potatoes does not necessarily mean an individual will also be allergic to cooked potatoes. The cooking process alters the proteins in potatoes, which can sometimes lessen or completely eliminate the allergic response.
There are several potential allergens that may be present in potatoes and contribute to an allergic reaction. These include:
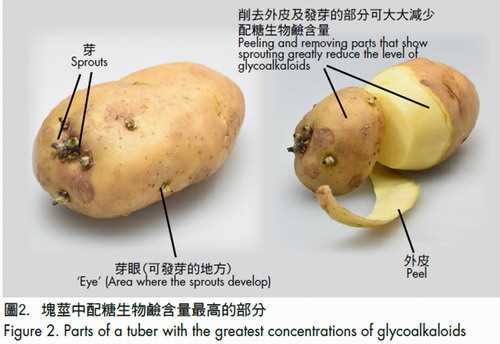
1. Glycoalkaloids
Glycoalkaloids are natural compounds found in potatoes, and solanine is one of the main glycoalkaloids responsible for their toxic properties. In some individuals, solanine can trigger an allergic response, resulting in symptoms such as itching, hives, or gastrointestinal distress.
2. Proteins
Potatoes contain several proteins that can potentially cause an allergic reaction. These proteins, such as patatin or the proteinase inhibitor PI-2, may trigger an immune response in sensitive individuals. Symptoms of a protein-related potato allergy can range from mild to severe and may include itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, or anaphylaxis in extreme cases.
It is worth noting that individuals who are allergic to any particular protein found in raw potatoes may not experience the same allergic reactions when the potatoes are cooked. The cooking process can denature some of these proteins, altering their structure and reducing their allergenic potential.
A visit to an allergist can help individuals determine if they have a potato allergy and whether it is specifically related to raw or cooked potatoes. Allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, may be conducted to identify the allergens causing the allergic reaction. Once identified, individuals can take appropriate measures to avoid exposure to those allergens and manage their potato allergy.
| Allergic Reaction | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Itchy Skin | Hives or rashes |
| Gastrointestinal Distress | Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea |
| Respiratory Issues | Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath |
| Anaphylaxis | Severe reaction, including difficulty breathing, rapid heart rate, and low blood pressure |
Questions and answers
Can you develop an allergy to raw potatoes, but not cooked?
Yes, it is possible to develop an allergy specifically to raw potatoes but not to cooked potatoes. Allergies can sometimes be triggered by certain proteins or substances in raw foods that are not present or are altered during the cooking process.
What are the symptoms of an allergy to raw potatoes?
The symptoms of an allergy to raw potatoes can vary from person to person, but commonly include itching or tingling in the mouth, swelling of the lips or throat, hives, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and difficulty breathing. In some cases, a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis can occur, which requires immediate medical attention.
Why would someone be allergic to raw potatoes but not cooked ones?
Some individuals may be allergic to specific proteins or substances present in raw potatoes that are altered or denatured during the cooking process. Heat can modify the structure of proteins, making them less likely to trigger an allergic reaction. Additionally, cooking may also break down certain compounds or compounds that cause allergies.
How is an allergy to raw potatoes diagnosed?
An allergy to raw potatoes can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and allergy tests such as skin prick tests or blood tests. These tests can help identify specific allergens or substances in raw potatoes that may be triggering an allergic reaction.
Can an allergy to raw potatoes develop later in life?
Yes, it is possible for an allergy to raw potatoes to develop later in life, even if a person has been able to eat them without any issues before. Allergies can develop at any age and can be triggered by various factors such as changes in the immune system or repeated exposure to certain substances.
Can someone be allergic to raw potatoes but not cooked?
Yes, it is possible for someone to be allergic to raw potatoes but not cooked. Some individuals may have a specific allergic reaction to certain proteins present in raw potatoes, while these proteins may be denatured or altered during the cooking process, making them less likely to cause an allergic reaction.






